The architecture
The Sophora Indexing Service is a scalable, self-coordinating multi-node service which uses several other services. Here's an overview of the architecture:
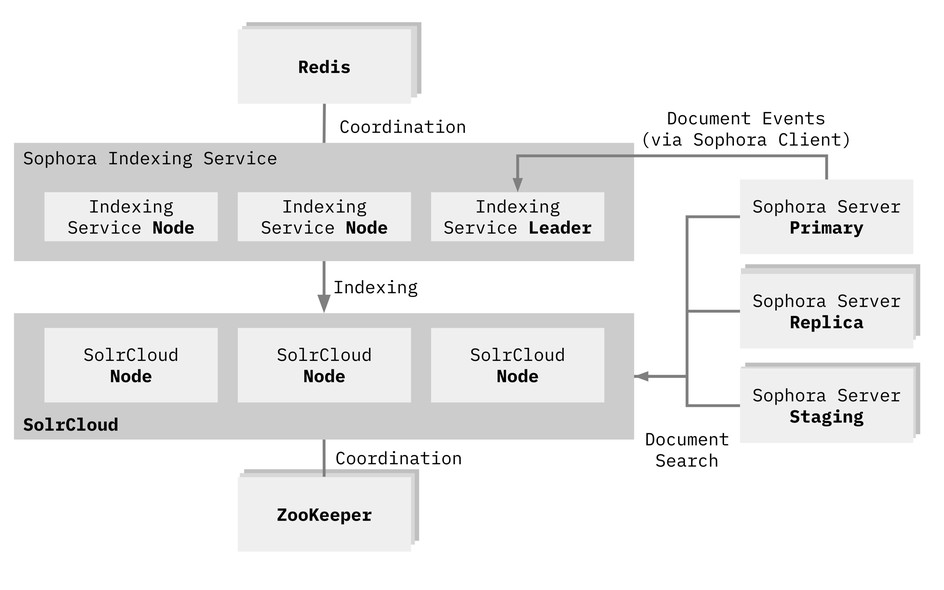
Some of the key concepts:
- The Sophora Indexing Service runs on several nodes. The Sophora Indexing Service instances coordinate with each other so that if one node fails, another can quickly take over
- The Sophora Indexing Service instances share a central, prioritized queue in a Redis database. The queue contains documents to be indexed including all necessary metadata
- One of the several instances of the Sophora Indexing Service is the leader. The leader instance updates the queue. If the leader changes, a new leader is being defined automatically
Sophora Indexing Service Requirements
The Sophora Indexing Service is based on open software standards and proven components.
The Sophora Indexing Service is a stand-alone Java app that requires an external SolrCloud cluster and a Redis Cluster. We recommend to use the following versions:
- Java: since version 4.6.0 use Java 17, otherwise Java 11. Java must be kept up to date with all updates and patches
- Redis: Version 7.0.9 or newer
- SolrCloud: Version 9.6 or newer
- ZooKeeper: Version 3.9.3 or newer (only if you manage SolrCloud yourself)
Deployment Guidelines
In productive environments, the Sophora Indexing Service should be scaled to at least two instances. One instance acts as the leader. In a failover scenario, the leader role is automatically assigned to another instance. The instances coordinate each other by using a Redis database.
Redis also acts as a centralized and prioritized working queue. All instances actively index SolrCloud, so that the overall indexing performance increases by the number of instances.
In development or testing environments, it is sufficient to run a single instance of the Sophora Indexing Service.
Configuration
The Sophora Indexing Service is a Spring Boot application and is therefore configurable by using an application.yaml file or through matching environment variables.
Application Configuration
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
spring.application.name | Name of the application | Sophora Indexing Service 👑 |
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include | Default Spring and custom endpoints that will be available to check certain application metrics under management.endpoints.web.exposure.base-path. | health, info, jolokia, prometheus, sophoraserver |
management.endpoints.web.exposure.base-path | Base path to expose application metrics. | / |
server.port | Server port of the Sophora Indexing Service. | 1837 |
sophora.indexingService.instanceGroupName | Sophora Indexing Service group name which identifies the current instance. The name is used as a prefix in Redis. | prod |
sophora.indexingService.solrConfigSetName | The name of the shared configset in Solr used for all Sophora collections. This can be used to easily manage the configuration for all Sophora collections. Available since 4.3.0. | |
sophora.indexingService.indexingTaskConsumer.numberOfThreads | Thread pool size for task consumption. | 5 |
sophora.indexingService.indexingEventConsumer.numberOfThreads | Thread pool size for event consumption. | 5 |
sophora.indexingService.taskBatchSize | Indexing jobs resulting from the same content change are combined into batches of this size. A higher batch size may result in a better overall performance, but also leads to less frequent updates. | 128 |
sophora.indexingService.derivedDocuments.grouping.addCommand | Defines whether commands are grouped into batches that add documents to an index. | true |
sophora.indexingService.derivedDocuments.grouping.deleteCommand | Defines whether commands are grouped into batches that delete documents from an index. | true |
sophora.indexingService.instanceGroupName | This label is exported via the Micrometer metrics and is part of the naming strategy for Redis. Multiple Sophora Indexing Service installations can share one Redis instance, if they use different instance group names. This approach is not recommended for productive environments. | prod |
sophora.indexingService.sync-delta-duration | When a new leader instance is selected or if all instances are down and then restarted, this delta is subtracted from the recorded sync date. The resulting date is then used to fetch and re-index all content changes missed. | 1h |
sophora.indexingService.max-retry-count | Maximum retries, if the processing of an event fails. When the maximum retry count is reached, the event will be discarded. | 100 |
sophora.indexingService.checkpoint-update-ms | SISI periodically determines and saves the modification date of the last synced document to SolrCloud, called a checkpoint. This property configures the checkpoint interval in ms. | 30000 |
sophora.indexingService.cleanup.placeholders.cron | Cron expression that defines when the cleanup process executes. | 0 0 0 * * ? |
sophora.indexingService.cleanup.placeholders.age | Duration expession (1d, 2h, etc) that describes the minimum age before internal solr documents will be deleted. These old internal solr documents are not your sophora documents but rather indexing meta information that is no longer needed. | 1d |
sophora.indexingService.cleanup.redis.cron | Cron expression that defines when the redis cleanup process executes. | 0 0 0 * * ? |
Configuration of the Sophora Client Connecting to the Sophora Server
The configuration options for the connection to the Sophora Server are listed in the Spring Boot Sophora Commons documentation.
Please note the new default values for some configurations:
| Property | Default |
|---|---|
sophora.client.cache.documentCacheElementsInMemory | 1000 |
sophora.client.cache.publishedDocumentCacheElementsInMemory | 1000 |
sophora.client.misc.update-interval | 1500 |
Solr & Redis Connection Configuration
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
sophora.solr.zk-hosts | A comma seperated list with no whitespace of at least one ZooKeeper host and port. Provide the chroot (e.g. "/solr") at the end if is not the zookeeper root directory. Examples:
| - |
sophora.solr.username | Solr user name, if the SolrCloud Basic Authentication Plugin is enabled | - |
sophora.solr.password | Solr password, if the SolrCloud Basic Authentication Plugin is enabled | - |
sophora.solr.connectionTimeout | Solr connection timeout in ms. | 15000 (15 seconds) |
sophora.solr.socketTimeout | Solr socket timeout in ms. | 120000 (2 minutes) |
spring.redis.redisson.config | Redis configuration object as a string. Please make sure to append |- to the configuration name, so that the Redisson configuration is being read as a multi line string (spring.redis.redisson.config: |-). Read more about advanced configuration options in the official Redisson documentation. | singleServerConfig:For versions < 4.6.0: singleServerConfig: |
sophora.indexingService.solrCluster.shards | Number of SolrCloud shards per collection. This config only applies the first time the collection is created. | 1 |
sophora.indexingService.solrCluster.replicationFactor | Number of SolrCloud replicas per collection. This config only applies the first time the collection is created. | 1 |
sophora.indexingService.solrCluster.autoAddReplica | If a SolrCloud node is down and autoAddReplica is set to true, a new replica is created if possible. If the old node comes back online, the newly created replica unloads and moved to the previous node. This config only applies the first time the collection is created. | false |
Logging Configuration
| Property | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
logging.level.root | The base logging level that is used, if the level is not overridden by a more specific rule. | |
logging.level.[package] | Example: com.subshell.sophora.indexingservice.*: DEBUG | |
logging.file.name | File name of the log file. |
Basic Configuration
The following basic application.yaml configuration gets you started. The configuration includes the most important configuration properties.
spring:
redis:
redisson:
config: |-
singleServerConfig:
address: "redis://127.0.0.1:${REDIS_PORT:6379}"
codec: !<com.subshell.sophora.indexingservice.core.codec.SISIJsonJacksonCodec> {}
# version < 4.6.0:
# codec: !<com.subshell.sophora.indexingservice.dataaccess.queue.redis.BetterJacksonCodec> {}
server:
port: 1837
sophora:
solr:
zk-hosts: localhost:2181/solr # add all available solr zookeeper hosts here
username: <solr-username>
password: <solr-password>
indexingService:
solrConfigSetName: sophora
instanceGroupName: dev
indexingTaskConsumer:
numberOfThreads: 5
indexingEventConsumer:
numberOfThreads: 5
max-retry-count: 100
client:
server-connection:
urls: "https://my-sophora-server:1195"
username: <sophora-username>
password: <sophora-password>
misc:
update-interval: 1500
cache:
documentCacheElementsInMemory: 500
publishedDocumentCacheElementsInMemory: 500
logging:
level:
root: INFO
com.subshell.sophora.indexingservice.*: DEBUG
file:
name: ./logs/sisi.log
Installation
Before installing the Sophora Indexing Service make sure that all external software dependencies have been installed correctly. The application.yaml should be located next to the Sophora Indexing Service jar file. Use the following command to start the Sophora Indexing Service or refer to the Spring Boot executable jar format documentation for a more advanced setup:
java -jar sophora-indexing-service-app-4.x.x.jar
Sophora Indexing Service Dependencies
The Sophora Indexing Service requires an external SolrCloud cluster and a Redis cluster. These external services are not directly part of the Sophora Indexing Service and should be managed by your administration team.
The following sections provide recommendations to configure them. Previous versions of Sophora used an embedded Solr version.
To configure the Sophora Server in a way that it uses the external SolrCloud, refer to the Sophora configuration documentation.
SolrCloud
SolrCloud is the cluster version of the open-source enterprise search platform Apache Solr. Setting up SolrCloud depends on your environment. SolrCloud requires a highly available Apache ZooKeeper cluster that manages the running Solr nodes and shared configuration files.
Most SolrCloud parameters are configurable via environment parameters (like SOLR_OPTS), using the Solr API or as a ZooKeeper configuration file. A basic SolrCloud and ZooKeeper installation process is described here.
SolrCloud Configuration
We recommend to use one Solr configset for all collections used by Sophora. The Sophora Indexing Service will create the collections with the configset defined by the sophora.indexingService.solrConfigSetName property. Existing Sophora collections will not be modified by the Sophora Indexing Service and need to be updated manually to use the configured configset.
For an optimal performance the solrconfig.xml needs to be adjusted (see the next section for details). The rest of the files in the configset can remain untouched.
Adjusted solrconfig.xml
In the solrconfig.xml we recommend to use autoSoftCommit with a maxTime configuration of 30000 and autoCommit with a maxTime of 60000 and with openSearcher set to false. It is also required to set the maxBooleanClauses configuration to 10000.
The Sophora Indexing Service in versions 4.2.0 and newer requires a modification to Solr's default solrconfig.xml to enable the feature Document Centric Versioning Constraints.
The section on the updateRequestProcessorChain by default looks like this:
<updateRequestProcessorChain name="add-unknown-fields-to-the-schema" default="${update.autoCreateFields:true}" processor="uuid,remove-blank,field-name-mutating,parse-boolean,parse-long,parse-double,parse-date,add-schema-fields">
<processor class="solr.LogUpdateProcessorFactory"/>
<processor class="solr.DistributedUpdateProcessorFactory"/>
<processor class="solr.RunUpdateProcessorFactory"/>
</updateRequestProcessorChain>
It has to be adjusted to look like this instead:
<updateRequestProcessorChain name="add-unknown-fields-to-the-schema" default="${update.autoCreateFields:true}" processor="uuid,field-name-mutating,parse-boolean,parse-long,parse-double,parse-date,add-schema-fields">
<processor class="solr.LogUpdateProcessorFactory"/>
<!-- Important: DocBasedVersionConstraintsProcessorFactory has to be right before DistributedUpdateProcessorFactory-->
<processor class="solr.DocBasedVersionConstraintsProcessorFactory">
<str name="versionField">sophora_versionconstraint_l</str>
<bool name="ignoreOldUpdates">true</bool>
<str name="deleteVersionParam">sophora_versionconstraint</str>
<bool name="supportMissingVersionOnOldDocs">true</bool>
</processor>
<processor class="solr.DistributedUpdateProcessorFactory"/>
<processor class="solr.RunUpdateProcessorFactory"/>
</updateRequestProcessorChain>
Here, we add additional processers like solr.DocBasedVersionConstraintsProcessorFactory, but also remove the remove-blank processor from the processor attributes. The rest of the configuration can stay default.
SolrCloud versions from 9.7 onwards come with a limitation of the number of fields per document (default is 1000). If you plan to have documents with more than 1000 fields, you may need to modify the NumFieldLimitingUpdateRequestProcessorFactory update processor. If the default configuration is used those documents will be rejected by SolrCloud and therefore not saved.
The processor accepts two parameters: the maximum number of fields and a warnOnly flag (default is false) which determines the behaviour of SolrCloud if the maximum number of fields is exceeded (please note that this flag only works correctly since SolrCloud version 9.9).
It is also possible to remove this feature completely by removing the NumFieldLimitingUpdateRequestProcessorFactory update processor and its name from the updateRequestProcessorChain.
ZooKeeper
To setup a ZooKeeper ensemble, please refer to the SolrCloud documentation.
Securing ZooKeeper with ACLs
If you want to set up ZooKeeper with ACLs on the SolrCloud ZK nodes you will need to pass the ACL credentials to the Indexing Service through one of the following options:
- as VM arguments, for example:
-DzkDigestUsername=user-readonly -DzkDigestPassword=onlyread -DzkCredentialsProvider=org.apache.solr.common.cloud.VMParamsSingleSetCredentialsDigestZkCredentialsProvider - in the environment variable
SOLR_ZK_CREDS_AND_ACLScontaining all the required VM arguments
Using the environment variable is our recommended approach for deployments in containers. Consult the SolrCloud and ZooKeeper documentation for more information about ACLs.
Authentication and Authorization
To enable basic role based authentication the Solr authentication plugin is required.
The authentication and authorization data is part of a security.json file that is located in the ZooKeeper root directory. The file might look like this:
{
"authentication": {
"blockUnknown": true,
"class": "solr.BasicAuthPlugin",
"credentials": {
"solr": "IV0EHq1OnNrj6gvRCwvFwTrZ1+z1oBbnQdiVC3otuq0= Ndd7LKvVBAaZIF0QAVi1ekCfAJXr1GGfLtRUXhgrF8c="
}
},
"authorization": {
"class": "solr.RuleBasedAuthorizationPlugin",
"permissions": [{
"name": "security-edit",
"role": "admin"
}
],
"user-role": {
"solr": "admin"
}
}
}
Adding the file to ZooKeeper is simple:
bin/solr zk cp file:path_to_local_security.json zk:/security.json -z localhost:9983
SolrRocks.Recommendation: Using Solr's Rule-Based Authorization Plugin to Control Direct Access to Solr
The Sophora APIs encapsulate access to Solr and ensure that apps on Sophora Staging Servers can only search live content. However, it is technically possible to access Solr directly from (web) apps and also access offline and working content.
To prevent this from happening, we recommend that you use Solr's Rule-Based Authorization Plugin. (See the documentation: https://solr.apache.org/guide/8_1/rule-based-authorization-plugin.html.)
Web apps should be required to use a dedicated user in Solr that does not have access to the non-live collections. This is accomplished through rule-based permission definitions which are assigned to users. The roles are customizable, and provide the ability to limit access to specific collections.
We recommend you to configure at least three roles:
- Write - has write access to both working and live content. This role should be reserved to the Indexing Service itself.
- Live - has read access only to live content. This role should be used for web apps and Sophora Staging Servers.
- Preview - has read access only to all content. This role should be used for Sophora Primary/Replica Servers.
To be able to create redirects programmatically, web apps need to access some offline content. We recommend configuring an Offline Core in Solr for web app access containing only information that is absolutely necessary.
SolrCloud Authentication and Authorization for the Sophora Server
The Sophora Server offers several search APIs that use the SolrCloud internally. As a result, the Sophora Server has to be authenticated in the SolrCloud as well. The Solr user name and password to be used by the Sophora Server must be configured.
Please refer to the section "SolrCloud" of the Sophora Server documentation for further information.
Sophora Staging Servers should use a Solr user, which has only the Live role. If the search API of a Sophora Staging Server is used, the server ensures that only live collections are accessed.
Redis
We recommend a minimum of three Redis cluster nodes to provide high availability and a failsafe setup.
We also recommend using a Redis cluster in sentinel mode to ensure automatic leader election, if a master node fails.
The Sophora Indexing Service currently does not support a multi-master Redis setup.
Example of a Sophora Indexing Service Deployment with Docker Compose
The example deployment setup includes one Redis instance, a SolrCloud installation with two instances, a ZooKeeper with one instance, and the Sophora Indexing Service with one instance.
The example was tested on Unix host machines. The deployment uses the following ports on the host machine:
| Service | Port |
|---|---|
| Solr 1 | 8983 |
| Solr 2 | 8984 |
| ZooKeeper | 2181 |
| Redis | 6379 |
| Sophora Indexing Service | 1837 |
The setup requires a Sophora Server to connect to. The connection parameters must be configured in the application.yaml of the Sophora Indexing Service.
docker-compose.yaml
version: '3.7'
services:
solr1:
image: solr:9.0
container_name: solr1
ports:
- "8983:8983"
volumes:
- "solr1:/var/solr"
environment:
- ZK_HOST=zoo1:2181/solr
- SOLR_PORT=8983
- SOLR_OPTS=-Dsolr.max.booleanClauses=10000 -Dsolr.autoSoftCommit.maxTime=30000
networks:
- solr
depends_on:
- zoo1
restart: on-failure
solr2:
image: solr:9.0
container_name: solr2
ports:
- "8984:8984"
volumes:
- "solr2:/var/solr"
environment:
- ZK_HOST=zoo1:2181/solr
- SOLR_PORT=8984
- SOLR_OPTS=-Dsolr.max.booleanClauses=10000 -Dsolr.autoSoftCommit.maxTime=30000
networks:
- solr
depends_on:
- zoo1
restart: on-failure
zoo1:
image: zookeeper:3.6.3
container_name: zoo1
hostname: zoo1
ports:
- 2181:2181
environment:
ZOO_MY_ID: 1
ZOO_SERVERS: server.1=0.0.0.0:2888:3888;2181
ZOO_4LW_COMMANDS_WHITELIST: "*"
networks:
- solr
redis:
container_name: redis
image: redis:6.2.4-alpine
ports:
- 6379:6379
networks:
- solr
volumes:
- "redis:/data"
sisi:
image: docker.subshell.com/sophora/sophora-indexing-service
container_name: sisi
volumes:
- "./application.yaml:/app/config/application.yaml"
ports:
- "1837:1837"
networks:
- solr
depends_on:
- solr1
- solr2
- redis
networks:
solr:
volumes:
solr1:
solr2:
redis:
Configuration
The example requires an external configuration file for the Sophora Indexing Service.
The configuration file must be placed in the file application.yaml, which must be reside in the same folder as the docker-compose.yaml.
The configuration may look like this:
spring:
application:
name: Sophora Indexing Service
jmx:
enabled: false
jackson:
mapper:
ACCEPT_CASE_INSENSITIVE_ENUMS: true
redis:
redisson:
config: |-
singleServerConfig:
address: "redis://redis:6379"
codec: !<com.subshell.sophora.indexingservice.core.codec.SISIJsonJacksonCodec> {}
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health, info, jolokia, prometheus, sophora
base-path: /
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
show-components: always
file:
path: logs
metrics:
tags:
application: Sophora Indexing Service
server:
port: 1837
sophora:
solr:
zk-hosts: zoo1:2181/solr
username: solr
password: solr
indexingService:
taskBatchSize: 128
solrConfigSetName: sophora
instanceGroupName: prod
indexingTaskConsumer:
numberOfThreads: 8
indexingEventConsumer:
numberOfThreads: 4
derivedDocuments:
grouping:
addCommand: true
deleteCommand: true
max-retry-count: 100
syncDeltaDuration: 1h
client:
server-connection:
urls: "http://hostname:1196"
username: "admin"
password: "admin"
cache:
documentCacheElementsInMemory: 1000
publishedDocumentCacheElementsInMemory: 1000
misc:
update-interval: 1500
springdoc:
swagger-ui:
path: "/"
doc-expansion: none
tags-sorter: alpha
operations-sorter: alpha
logging:
level:
root: INFO
com.subshell.sophora.indexingservice.*: DEBUG
SolrCloud
It is sufficient to back up SolrCloud. Please consider the SolrCloud documentation for further information about the backup and recovery process of SolrCloud.